Currently, there is quite a buzz in the web hosting industry about the confusion about technological differences between Cloud Hosting vs VPS Hosting, and there has been a lot of discussion about it.
The basic difference between the two is generally misunderstood by most people as they tend to confuse the two. The reason for this is that most people are unaware of the key differences between these two technologies when it comes to web hosting.
Increasingly, as a result of the advent of virtualization and remote operations, there has been an increase in the number of established organizations and even startups opting for similar solutions to host their websites.
This means that they do not need to purchase a physical architecture (a processor with certain specifications of processors, RAM, and storage), an operating system that runs on top of this hardware, and a web application that will be used to host the website (like WordPress, Magento, Drupal, Joomla, and many others, etc.) anymore.
VPS Hosting
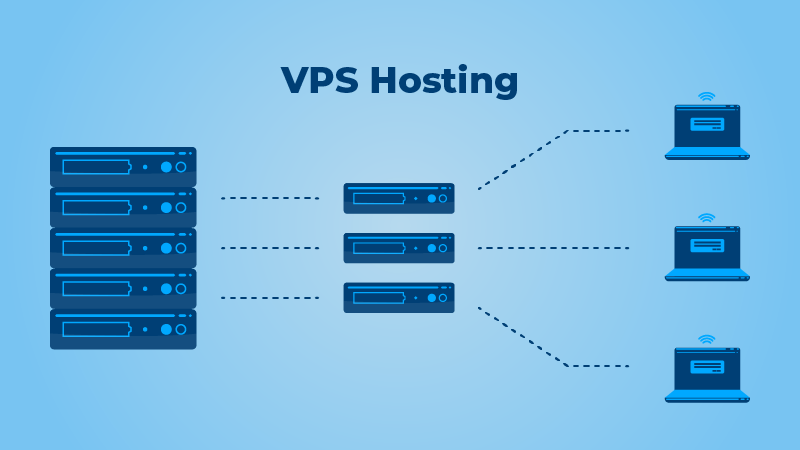
A VPS is an acronym for a Virtual Private Server. This type of hosting consists of one physical server, divided into several smaller virtual servers, which are all on the same physical server.
Despite the fact that these virtual servers are physically located on the same server, each one of them acts as its own dedicated server in the cloud infrastructure.
The reason for this is that you have your own dedicated section on the server, so you have your own set of allocated resources and can customize and configure your partition of the server exactly the way you want it.
Additionally, a VPS server doesn’t allow data to be exchanged between accounts or file access to be granted between accounts. In spite of these risks, VPS hosting comes with the risk of failure of one physical server if it fails, resulting in the failure of every VPS that is using it.
In addition, you may also experience fluctuations in the performance of your VPS if one site happens to hog the resources of the physical server. However, most hosting companies partition the different sections of their VPS in a way that eliminates this risk.
Cloud Hosting
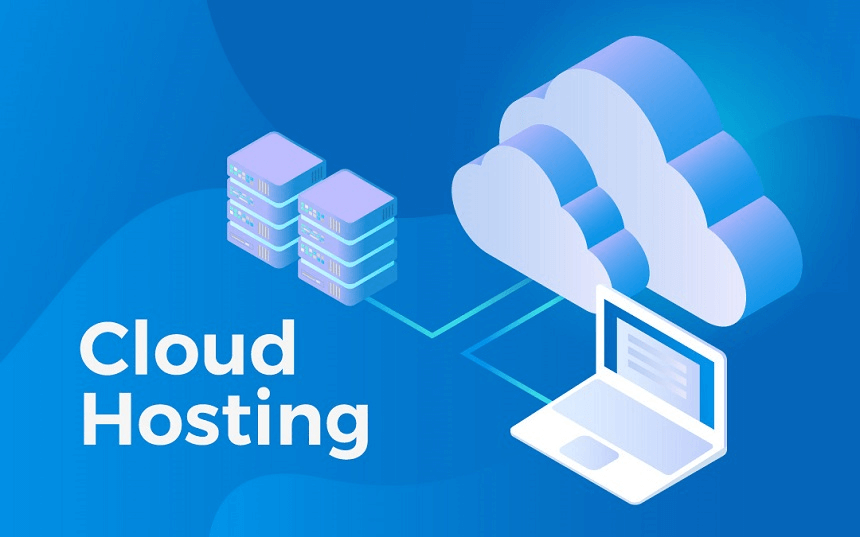
In terms of website (or application) hosting solutions, cloud hosting is the top-of-the-line service available presently. It has only taken a short period of time for the technology to gain enormous acceptance, and it has already been very successful.
Cloud-hosted websites can be accessed at any time, from any location, without any restrictions. There is a replication of hosting resources for each website within the cluster of cloud servers so that each website is hosted on a separate server.
It is, for example, capable of routing the query for a specific site automatically to an idle cloud server in a cluster if one cloud server currently has maximum traffic.
Essentially, what happens in the cloud is that it runs the web hosting services such as file storage, SSH, FTP, and SFTP, as well as the email services (e.g., SMTP), etc., on many different servers simultaneously.
There is a great deal of reliability provided by this simultaneous allocation of the same resources across all of the cloud servers in the cluster. It is important to remember, for example, that if one of the machines malfunctions, it will not result in a failure of the entire hosting service.
Benefits of VPS Hosting
- There is no limit to the freedom you can enjoy with VPS hosting. It is entirely up to you how your server is managed, everything is accessible, and you are able to install as much software as you would like.
- It is very efficient to host your website on a virtual private server. It is important to note that VPS hosting is not dependent upon traffic or audience like shared hosting. Your server is isolated from other servers, so you have your own resources.
- It is safe and secure to host your website on a VPS. No matter what privileges a client may have on the server, all of your files are private and inaccessible to others.
Benefits Of Cloud Hosting
- The reason that cloud hosting is relatively reliable is that it uses multiple physical networks to host your website on a virtual partition. A server going offline will lower the cloud’s resource level slightly, but it won’t impact your website. There is no inaccessibility or anything else.
- Several physical servers secure cloud hosting so that third parties cannot access their premises or interrupt their services.
- There are many benefits of cloud hosting, including its extensibility, flexibility, and scalability. As opposed to a single server, it does not have the same constraints that a multi-server has. Depending on your request, resources are made available in real-time.
- There are many benefits associated with cloud hosting, including the fact that you only pay for what you use.
The Differences Between Cloud and VPS
Scalability
There is one thing that is often criticized about Virtual Private Servers, and that is the fact that they do not scale well. On the other hand, a cloud’s infrastructure allows it to scale up or down according to the demand that it faces. By scaling your server vertically, you are able to have the capacity to handle any growth that comes your way in the future. There is no need to reboot when you can automatically provision and augment RAM, bandwidth, and computing resources on the fly, without the need to reboot.
High Availability
Due to its ability to provide failover protection, cloud computing wins when it comes to maximizing availability. Your virtual server is always online in the cloud infrastructure, so you can access it at any time.
There is no need for a server to go down in order to share a load of another server in the infrastructure if a server goes down. VPSs, on the other hand, are not capable of doing this since they are only equipped with virtualization software, which is based on a hypervisor, which can result in downtime.
Multiple servers are used in a cloud setup so that virtual machines can be hosted and managed by using a hypervisor that runs on the server. For complete data durability and redundancy, you can deploy multiple backup servers using on-demand backup.
Custom Infrastructure
Despite the fact that virtually all providers offer some form of customization on their VPS plans, cloud servers are a whole ‘another level in terms of customization.
Create your own template or choose from hundreds of OS and app templates. Set up tiered storage with multiple SANs per cloud, and choose what amount of storage you need based on what you need. In addition to these customizable tools and frameworks, many additional add-ons can be included, such as automatic load balancers and anti-spoof firewalls, to name just a few.
Final Word
It is important to understand that the setup of a traditional Virtual Private Server and a Cloud Server is very similar. The main difference between the two is the way each server is deployed and managed.
The difference between a VPS and a cloud server is that a VPS resides on one single physical server, while a cloud server is based on multiple physical servers for maximum scalability and high availability.
